Management of bioproducts and NPK fertilization in maize grown on Eutric Nitisols in Cuba
Main Article Content
Abstract
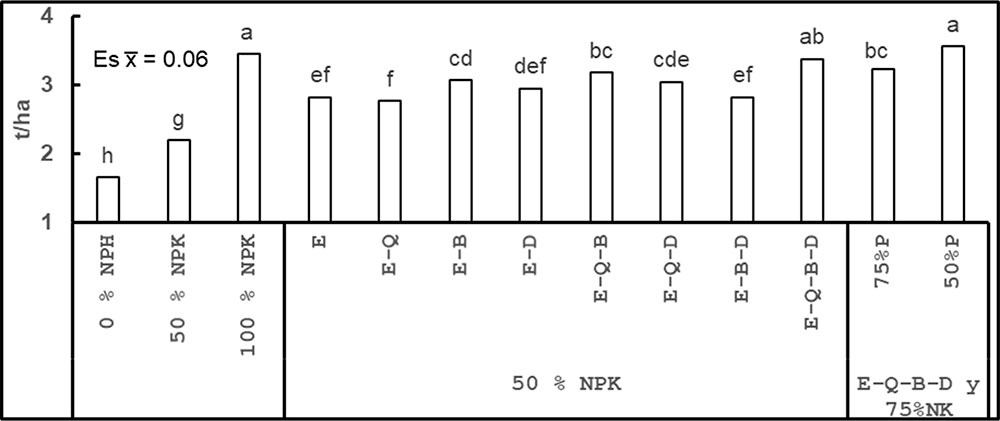
Maize is an important food source for both humans and livestock. In Cuba, its production is limited by insufficient nutrient supply; however, various bioproducts have been developed that either provide nutrients or enhance their utilization efficiency. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the combined application of several bioproducts in relation to fertilizer doses and the maximum experimental yields of maize grown on Eutric Nitisols. Three experiments were conducted with different cultivars during the 2009-2015 period. Randomized block designs were used to assess various combinations of the bioproducts EcoMic®, Biobras-16®, Fitomas-E®, Quitomax®, and Dimargon®, with up to four bioproducts applied in the presence of different NPK fertilizer doses, as well as treatments with fertilizer alone. A beneficial response to the combined application of bioproducts was observed, depending on the fertilizer dose and the maximum yield obtained. For yield levels between 3 and 4 t ha⁻¹, applying 50 % NPK was sufficient. When yield increased to 5 t ha⁻¹ and in soils with high available phosphorus content, the dose should be increased to 75 % NK, while maintaining phosphorus at 50 %, since applying 75 % P reduced the yield of the bioproduct combination. The application of bioproducts in the presence of 50 % NPK fertilization consistently achieved yields similar to those obtained with 100 % NPK.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors who have publications with this journal accept the following terms of the License Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0):
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
The journal is not responsible for the opinions and concepts expressed in the works, they are the sole responsibility of the authors. The Editor, with the assistance of the Editorial Committee, reserves the right to suggest or request advisable or necessary modifications. They are accepted to publish original scientific papers, research results of interest that have not been published or sent to another journal for the same purpose.
The mention of trademarks of equipment, instruments or specific materials is for identification purposes, and there is no promotional commitment in relation to them, neither by the authors nor by the publisher.
References
Oficina Nacional de Estadísticas e Información. Anuario estadístico de Cuba 2022. Agricultura, Ganadería, Silvicultura y Pesca (Capítulo 9). Oficina Nacional de Estadísticas e Información. 2023. Available from: http://onei.gob.cu/anuario-estadistico-de-Cuba-2022
Dibut Álvarez B, Martinez Viera R, Hernández Barrueta G, López Gutiérrez M, Martínez Cruz A, Bach Álvarez T, Rivera Espinosa R, Hernández Rodríguez A, Fernández Martín F, Medina Basso N, Herrera Peraza R. Surgimiento y desarrollo en Cuba de la red de producción de biofertilizantes y bioestimuladores. Agrotecnia de Cuba. 2011; 35 (1): 61-72. Available from: https://agrotecnia.edicionescervantes.com/index.php/agrotecnia/article/view/433
Rivera R, González P J, Ruiz-Martinez L, Martin G, Cabrera A. Strategic Combination of Mycorrhizal Inoculants, Fertilizers, and Green Manures Improve Crop Productivity. Review of Cuban Research. In Qiang-Sheng Wu, Ying-Ning Zou, Yue-Jun He, Nong Zhou, editors. “New Research on Mycorrhizal Fungus”. Nova Publishers, USA. 2023. (eBook). Available from: Doi: http://doi.org/10.52305/GLXN2905
Morales-Mena B, Hernández-Forte I, Nápoles-García M C. Estabilidad microbiológica de los biofertilizantes Azofert®-F y Azofert®-S. Cultivos Tropicales. 2023; 44(3). https://cu-id.com/2050/v44n3e03. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/1734
Falcón Rodríguez A B, Costales Menéndez D, González-Pena Fundora D, Nápoles García M C. Nuevos productos naturales para la agricultura: Las oligosacarinas. Cultivos Tropicales. 2015; 36(5 Esp), 111-129. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article /view/1128Cul.tivos
Salazar S M, Coll Y, Viejobueno J, Coll F. Response of strawberry plants to the application of brassinosteroid under field conditions. Rev. Agron. Noroeste Argent. 2016; 36 (1): 37-41. Available from: https://repositorio.inta.gob.ar/handle/20.500.12123/5238
Gaceta Oficial de la República de Cuba. Decreto-ley 64 “De la producción, desarrollo y uso de los biofertilizantes, bioestimulantes y bioplaguicidas de uso agrícola”. GOC-2023-515-O53. Available from: https://www.gaceta/oficial.gob.cu/es/gaceta-oficial-no-53-ordinaria-de-2023.
Departamento de Suelos y Fertilizantes. (2020). Manual práctico para uso de bioproductos y fertilizantes líquidos. Ministerio de la Agricultura de Cuba. Available from: https://es.scribd.com/document/501110234/Manual Biofertilizantes y Fertilizantes Liquidos V 10-1-2020 | PDF | Fertilizante | Siembra
Shi J, Wang X, Wang E. Mycorrhizal symbiosis in plant growth and stress adaptation: from genes to ecosystems. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 2023; 74: 569-607. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-061722-090342
Fiorilli V, Martinez-Medina A, Pozo M J, Lanfranco L. Plant immunity modulation in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis and its impact on pathogens and pests. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 2024; 62(1):127-56. Available from: Doi http://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-121423-042014
Kasanke S A, Cheeke T E, Moran J J, Roley S S. Tripartite interactions among free-living, N-fixing bacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and plants: Mutualistic benefits and community response to co-inoculation. Soil Science Society of America Journal. 2024; 88: 1000-13. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/saj2.20679
Wang Q, Li S, Li J, Huang D. The utilization and roles of nitrogen in plants. Forests. 2024; 15, 1191. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071191
Bertsch F. Absorción de nutrimentos por los cultivos. 1 era edición, San José, C.R. ACCS; 2003. Available from: https://books.google.com/books/about/Absorci%C3%B3n_de_nutrimentos_por_los_cultiv.html?id=by_FAAAACAAJ
Reinprecht Y, Schram L, Marsolais F, Smith T H, Hill B, Pauls K P. Effects of Nitrogen Application on Nitrogen Fixation in Common Bean Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2020; 11:1172. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.01172
Antil R S, Raj D. Integrated nutrient management for sustainable crop production and improving soil health. In R. S. Meena (Ed.), Nutrient dynamics for sustainable crop production2020: 67-101. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8660-2_3.
Corbera J G, Nápoles M C. Efecto de la inoculación conjunta Bradyrhizobium elkanii-Hongos MA y la aplicación de un bioestimulador del crecimiento vegetal en soya (Glycine max (L.) Merrill), cultivar INCASOY-27. Cultivos Tropicales. 2013; 34(2): 5-11. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/418
Gonzalez-Cañizares P J, Ramirez-Pedroso J, Rosseaux R, Rivera R. Biofertilización con Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus y Funneliformis mosseae en pasto guinea (Megathyrsus maximus vc. Likoni). Nota técnica. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science. 2022; 56(3): 201-6. Available from: https://cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/1059/1419
González-Cañizares, P. J., Méndez-Bonet, S., Reyes-Rouseaux, R., Rivera-Espinosa, R., & Hernández-Jiménez, A. Integrated management of the fertilization for Tithonia diversifolia forage production. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science. 2024; 58. Available from: https://cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/1146
Morejón-Pereda M, Herrera-Altuve J A, Ayra-Pardo C, González-Cañizares P J, Rivera-Espinosa R, Fernández-Parla Y, Peña-Ramírez E, Rodríguez P, Rodríguez-de la Noval C, de la Noval-Pons B. Alternatives in the nutrition of transgenic maize FR-Bt1 (Zea mays L.): response in growth, development, and production. Cultivos Tropicales. 2017; 38(4), 146-55. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/1414.
Witt C, Buresh R J, Peng S, Balasubramanian V, Doberman A. Nutrient Management. In: T. Fairhust; C. Witt; R. Buresh, A. Doberman, editors. Rice: A practical guide to nutrient management. 2nd Ed. International Rice Research Institute, International Plant Nutrition Institute, and International Potash Institute. 2007. Available from: https://www.ipipotash.org/publications/publication-229
Rivera R, Cabrera Rodriguez A, Martin Alonso G M, Fundora Sanchez L R. Bioproductos y fertilización NPK en el frijol cultivado sobre suelos Ferralíticos Rojos Lixiviados. Cultivos Tropicales. 2025; 46 (3). Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/1881
Hernández A, Pérez J, Bosch D, Castro N. Clasificación de los suelos de Cuba. Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Agrícolas, Cuba: Ediciones INCA. 2015. Available from: https://isbn.cloud/9789597023777/clasificacion-de-los-suelos-de-cuba-2015/
IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. 4th edition. International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS), Vienna, Austria. 2022. Available from: https://wrb.isric.org/documents/ WRB_fourth_edition_2022-12-18.pdf
Paneque V M, Calaña J M, Calderón M, Borges Y, Hernández T C, Caruncho C M. Manual de Técnicas analíticas para Análisis de suelo, foliar, abonos orgánicos y fertilizantes químicos Ediciones Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Agrícolas. Mayabeque, Cuba. 2010. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/files/folletos/ folleto_ suelos.pdf
Torres-Arias Y, Ortega-Fors R, González González S, Furrazola Gómez E. Diversidad de hongos micorrizógenos arbusculares (Glomeromycota) en bosques semicaducifolios de la Ciénaga de Zapata, Cuba. Revista Del Jardín Botánico Nacional. 2015; 36: 195-200. Available from: https://revistas.uh.cu/rjbn/article/view/7082
MINAG. 1984. Manual de interpretación de los índices físico-químicos y morfológicos de los suelos cubanos. Editorial Científico-Técnica, Ciudad de La Habana, Cuba: 136 p.
Rivera R, Fernández Martín F, Ruiz Martínez L, González Cañizares P J, Rodríguez Yon Y, Pérez Ortega E, Fernández Suarez K, Martín Alonso G M, Simó González J, Sánchez Esmoris C, Riera Nelson M, de la Noval Pons B, et al. Lara Franqui D. Manejo, integración y beneficios del biofertilizante micorrízico EcoMic® en la producción agrícola. Ediciones Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Agrícolas, Mayabeque, Cuba; 2020. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/files/libros/del_biofertilizante_micorrízico.pdf
Rivera R, Martin G, Pérez A, González P J, Ramírez J, García-Rubido M, Ruiz M, Espinosa A, Reyes R, Fundora L R, Delgado A, Alarcón M, Wencomo H, et al. Establecimiento de un sistema para uso del biofertilizante micorrízico EcoMic® y otros bioproductos en la producción de alimentos. Informe Técnico Final del Proyecto FONCI 24-2018. 2020; 31 p. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.20798.51527
Lanfranco L, Bonfante P. The need for phosphate: at the root of the mycorrhizal symbiosis. Sci Bull (Pekín). 2022; 67(5):459-460. Available from: doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.11.018
Zhao B, Jia X, Yu N, Murray J D, Yi K, Wang E. Microbe-dependent and independent nitrogen and phosphate acquisition and regulation in plants. New Phytol. 2024; 242: 1507-22. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.19263
González Cañizares P J, Ramírez Pedroso J F, Morgan Rosemond O, Rivera Espinosa R, Plana Llerena R. Contribución de la inoculación micorrízica arbuscular a la reducción de la fertilización fosfórica en Brachiaria decumbens. Cultivos Tropicales. 2015; 36 (1) :135 -42. Available from: https://ediciones.inca.edu.cu/index.php/ediciones/article/view/952.