Effect of systemic fungicide on the presymbiotic growth of Rhizophagus irregularis (INCAM 11), in vitro
Main Article Content
Abstract
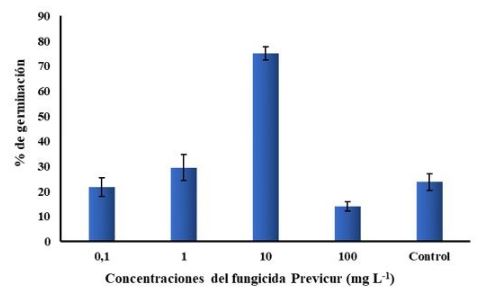
Fungicides are widely used in current culture systems to control or eliminate fungal plant pathogens. However, these chemicals can affect indigenous soil microorganisms, including those that promote plant growth, such as arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF). Considering the above exposed, the present study set out to determine the effect of different concentrations of the systemic fungicide Previcur energy 84 sl on the presymbiotic stage of Rhizophagus irregularis (INCAM 11), under in vitro culture conditions. Modified Strullu and Romand culture medium (SRM) was employed to evaluate percentage of germination, growth of germinating tube, as well as its percentages of increase and decrease, when studying four concentrations of the Previcur Fungicide (0,1; 1; 10 and 100 mg L-1). At 10 mg -1 a stimulating effect on germination and on the growth of the germ tube of the fungus. The present work constitutes the first evidence on the effect of a systemic fungicide in the presimbiotic stage of mycorrhizal fungus on in vitro conditions reported in Cuba.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors who have publications with this journal accept the following terms of the License Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0):
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
The journal is not responsible for the opinions and concepts expressed in the works, they are the sole responsibility of the authors. The Editor, with the assistance of the Editorial Committee, reserves the right to suggest or request advisable or necessary modifications. They are accepted to publish original scientific papers, research results of interest that have not been published or sent to another journal for the same purpose.
The mention of trademarks of equipment, instruments or specific materials is for identification purposes, and there is no promotional commitment in relation to them, neither by the authors nor by the publisher.
References
Alguacil M del M, Torres MP, Montesinos-Navarro A, Roldán A. Soil Characteristics Driving Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Communities in Semiarid Mediterranean Soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2016;82(11):3348-56. doi:10.1128/AEM.03982-15
Lanfranco L, Fiorilli V, Gutjahr C. Partner communication and role of nutrients in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. New Phytologist. 2018;220(4):1031-46. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15230
Cozzolino V, Di Meo V, Monda H, Spaccini R, Piccolo A. The molecular characteristics of compost affect plant growth, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and soil microbial community composition. Biology and Fertility of Soils. 2016;52(1):15-29. doi:10.1007/s00374-015-1046-8
Hage-Ahmed K, Rosner K, Steinkellner S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their response to pesticides. Pest Management Science. 2019;75(3):583-90. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5220
Lamichhane JR, You MP, Laudinot V, Barbetti MJ, Aubertot J-N. Revisiting Sustainability of Fungicide Seed Treatments for Field Crops. Plant Disease. 2019;104(3):610-23. doi:10.1094/PDIS-06-19-1157-FE
Battini F, Cristani C, Giovannetti M, Agnolucci M. Multifunctionality and diversity of culturable bacterial communities strictly associated with spores of the plant beneficial symbiont Rhizophagus intraradices. Microbiological Research. 2016;183:68-79. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.012
Declerck S, Strullu DG, Plenchette C. Monoxenic culture of the intraradical forms of Glomus sp. isolated from a tropical ecosystem: a proposed methodology for germplasm collection. Mycologia. 1998;90(4):579-85. doi:10.1080/00275514.1998.12026946
Hernández-Dorrego A, Mestre-Parés J. Evaluation of some fungicides on mycorrhizal symbiosis between two Glomus species from commercial inocula and Allium porrum L. seedlings. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research. 2010;8(1):43-50. doi:10.5424/sjar/201008S1-1222
Gerdemann JW, Nicolson TH. Spores of mycorrhizal Endogone species extracted from soil by wet sieving and decanting. Transactions of the British Mycological society. 1963;46(2):235-44.
Herrera RA, Ferrer RL, Furrazola E, Orozco MO. Estrategia de funcionamiento de las micorrizas VA en un bosque tropical. Biodiversidad en Iberoamérica. Ecosistemas, Evolución y Procesos sociales.(Eds. Maximina Monasterio) programa Iberoamericano de Ciencia y Tecnología para el desarrollo. Subprograma XII, Diversidad Biológica, Mérida. 1995;
Cranenbrouck S, Voets L, Bivort C, Renard L, Strullu D-G, Declerck S. Methodologies for in Vitro Cultivation of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi with Root Organs. In: Declerck S, Fortin JA, Strullu D-G, editors. In Vitro Culture of Mycorrhizas [Internet]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2005 [cited 05/10/2021]. p. 341-75. doi:10.1007/3-540-27331-X_18
Perera-García SS, Fernández-Suárez K, Pérez-Ortega EJ. Germinación y crecimiento de propágulos de Rhizoglomus sp. in vitro. Cultivos Tropicales [Internet]. 2019;40(2). Available from: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0258-59362019000200005&script=sci_arttext&tlng=en
Arocha-Rodríguez M de la C, Pérez-Ortega E, Fernández-Suárez K, Haesaert G. Efecto del pH del medio de cultivo en el crecimiento presimbiótico de Rhizoglomus irregulare. Cultivos Tropicales [Internet]. 2019;40(2). Available from: scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S0258-59362019000200008&script=sci_arttext&tlng=pt
Gray CD, Kinnear PR. IBM SPSS Statistics 19 Made Simple. Psychology Press; 2012. 688 p.
de Novais CB, Avio L, Giovannetti M, de Faria SM, Siqueira JO, Sbrana C. Interconnectedness, length and viability of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelium as affected by selected herbicides and fungicides. Applied Soil Ecology. 2019;143:144-52. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.06.013
Samarbakhsh S, Rejali F, Ardakani MR, Nejad FP, Miransari M. The combined effects of fungicides and arbuscular mycorrhiza on corn (Zea mays L.) growth and yield under field conditions. Journal of Biological Sciences. 2009;9(4):372-6.
Rose MT, Cavagnaro TR, Scanlan CA, Rose TJ, Vancov T, Kimber S, et al. Impact of Herbicides on Soil Biology and Function. In: Sparks DL, editor. Advances in Agronomy [Internet]. Academic Press; 2016 [cited 05/10/2021]. p. 133-220. (Advances in Agronomy; vol. 136). doi:10.1016/bs.agron.2015.11.005
Zocco D, Fontaine J, Lozanova E, Renard L, Bivort C, Durand R, et al. Effects of two sterol biosynthesis inhibitor fungicides (fenpropimorph and fenhexamid) on the development of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Mycological Research. 2008;112(5):592-601. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2007.11.010
Zocco D, Van Aarle IM, Oger E, Lanfranco L, Declerck S. Fenpropimorph and fenhexamid impact phosphorus translocation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza. 2011;21(5):363-74. doi:10.1007/s00572-010-0344-0
Rivera-Becerril F, van Tuinen D, Chatagnier O, Rouard N, Béguet J, Kuszala C, et al. Impact of a pesticide cocktail (fenhexamid, folpel, deltamethrin) on the abundance of Glomeromycota in two agricultural soils. Science of The Total Environment. 2017;577:84-93. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.098
Buysens C, Dupré de Boulois H, Declerck S. Do fungicides used to control Rhizoctonia solani impact the non-target arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis? Mycorrhiza. 2015;25(4):277-88. doi:10.1007/s00572-014-0610-7
Lekberg Y, Wagner V, Rummel A, McLeod M, Ramsey PW. Strong indirect herbicide effects on mycorrhizal associations through plant community shifts and secondary invasions. Ecological Applications. 2017;27(8):2359-68. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.1613